Plate heat exchanger (PHE) is a type of heat exchanger that uses metal plates sealed with gaskets to transfer heat between a hot fluid with a cold fluid. Liquid flowing through the PHE channels experiences turbulent flow at low velocities producing high heat transfer efficiency and low fouling which results in smaller and a compact unit. A PHE has wide industrial applications especially in HVAC, oil and gas, power generation, edible oil etc.
- Working Principle of a Plate Heat Exchanger
The plate heat exchanger works at a certain pressure if it is tightened to a minimum. The heat is transferred from one medium to another via a pressurized plate. Hot and cold mediums flow between each plate and then they exchange their heat without mixing with each other.
- Structure of PHE Plate
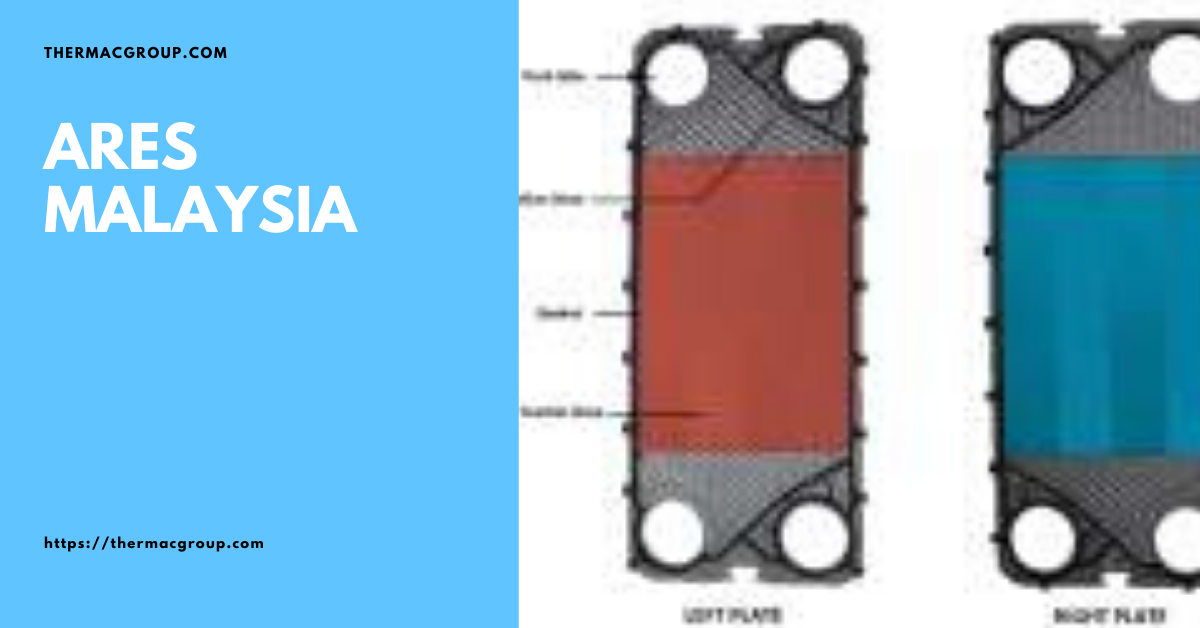
The plate is an important part of the plate heat exchanger. it is manufactured with a special design for the highest heat transfer rate. The material of the plates depends on the medium passing through the plate heat exchanger. It is very important that the medium must be suitable for plate material otherwise, aggressive medium can damage the plates.
- PHE Gaskets Design
Gaskets prevent simple mixing of each other. Gasket material varies depending on the application, NBR and EPDM is the most commonly used throughout the world for plate heat exchangers. Some other material such as FKM, Silicone or other special material may be used.
For more information about ARES Malaysia, please visit https://thermacgroup.com